This image provides a structured roadmap for learning how to build AI agents, divided into two main levels: “Basics of ML and GenAI” and “Deepdive into RAGs and AI Agents.” Here’s a blog post based on the steps outlined in the roadmap.

Your Ultimate Roadmap to Becoming an AI Agent Developer
The world of Artificial Intelligence is moving fast, shifting from simple chatbots to autonomous “AI Agents” that can plan, use tools, and solve complex problems. If you want to move from being a user to a builder, you need a structured path.
Here is a comprehensive roadmap to take you from the basics of code to deploying advanced multi-agent systems.
Level 1: The Foundations of Machine Learning and GenAI
Before you can build an agent, you must understand the engine that powers it.
1. Master the Programming Basics
Every AI journey starts with code. Focus on Python (the industry standard) and TypeScript (widely used for web-based AI integrations).
- Key Topics: Data types, Control structures (if/else, loops), File I/O, and Networking.
2. Understand Machine Learning Fundamentals
You don’t need to be a mathematician, but you must understand how models “learn.”
- Key Topics: Types of ML (Supervised/Unsupervised), Neural Networks, and Reinforcement Learning (which is critical for agent behavior).
3. Deep Dive into Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs are the “brains” of your agent. You need to know how they process information.
- Key Topics: Transformers architecture, Mixture of Experts (MoE), Fine-tuning, and managing Context Windows.
4. Master Prompt Engineering
The way you talk to a model determines how well it performs.
- Key Topics: Chain of Thought (CoT), Graph of Thoughts, Few-shot/Zero-shot learning, and Role-based prompting.
5. Explore API Wrappers
Most developers don’t run models locally; they connect to them via APIs.
- Key Topics: API Types, GPT-Wrappers, Authentication, and handling File I/O via API.
Level 2: Advanced Implementation (RAGs and AI Agents)
Once you understand the basics, it’s time to give your AI “memory” and the ability to “act.”
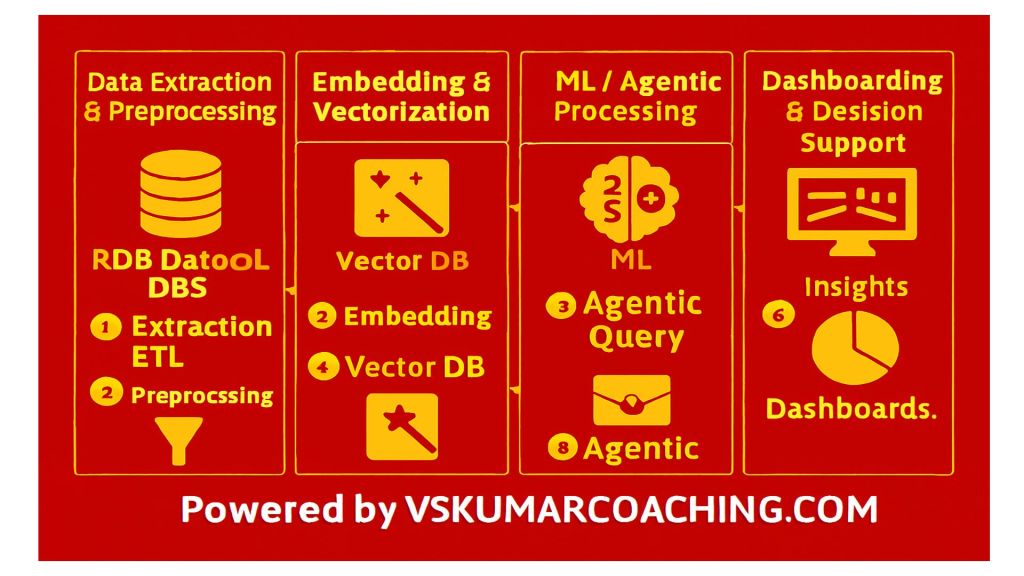
6. Basics of RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
RAG allows your AI to access private data or real-time information.
- Key Topics: Embeddings, Vector Stores (databases), Retrieval Models, and Generation Models.
7. Core AI Agent Concepts
This is where the AI becomes an “Agent”—an entity that can make decisions.
- Key Topics: Types of Agents, Design Patterns, Agent Memory, and Tools/MCP (Model Context Protocol).
8. AI Agent Frameworks
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Use frameworks to manage the complexity.
- Key Topics: Orchestration, Planning, Feedback loops, and Streaming responses.
9. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
The future belongs to groups of agents working together (e.g., one agent writes code while another tests it).
- Key Topics: Types of MAS, Communication Patterns, Hand-offs, and A2A (Agent-to-Agent) Protocols.
10. Evaluation and Observability
How do you know if your agent is actually good? You must measure its performance.
- Key Topics: Performance Metrics, Logging, Latency tracking, and Stress testing.
Conclusion: Ready for Liftoff
Following this roadmap ensures you aren’t just copy-pasting code, but building a deep understanding of how intelligent systems function. Once you’ve mastered evaluation and observability, you are ready to build, deploy, and scale “cool AI agents” that can change the way we work.
Where are you on your journey? Start at Level 1 and keep building!
To truly level up this roadmap, let’s look at how these technical skills translate into real-world impact. Transitioning from “Standard Automation” (Level 1) to “Autonomous AI Agents” (Level 2) isn’t just a tech upgrade—it’s a massive shift in business economics.
Here are four live-example domains showcasing the “Before” vs. “After” of agent conversion.
1. Customer Experience & Support
The Use Case: Managing high-volume e-commerce inquiries (returns, tracking, product advice).
- Current Issues (Without Agents): Relies on keyword-based chatbots that fail on nuance. Customers get stuck in “death loops” of irrelevant FAQs. Human staff spend 70% of their time on repetitive tickets like “Where is my order?”
- After Agent Conversion: Agents use RAG to check real-time shipping APIs and internal inventory. They don’t just “answer”—they act by initiating a refund or re-routing a package autonomously.
- Benefits & Savings: * 90% reduction in response time (from hours to seconds).
- 30% lower operational costs by deflective routine tickets.
- Live Example: Camping World reduced wait times from hours to 33 seconds using agentic routing.
2. Healthcare Administration
The Use Case: Clinical documentation and patient triage.
- Current Issues (Without Agents): Doctors spend 2+ hours daily on “pajama time” (manual data entry into EHR systems). Triage is handled by static forms that can’t detect the urgency of a patient’s tone or complex symptoms.
- After Agent Conversion: Ambient Scribe Agents listen to consultations and update medical records in real-time. Triage Agents analyze patient history + current symptoms to prioritize emergency cases.
- Benefits & Savings:
- 50% reduction in administrative burnout.
- Increased Revenue: Faster throughput allows clinics to see 2–3 more patients per day.
- Live Example: Annalise.ai acts as an agentic “spell-checker” for radiologists, flagging abnormalities in X-rays with higher precision than manual review.
3. Financial Services & Fraud
The Use Case: Real-time fraud detection and loan underwriting.
- Current Issues (Without Agents): Rule-based systems trigger high “false positives,” blocking legitimate transactions. Loan approvals take 3–5 days due to manual verification of pay stubs and tax returns.
- After Agent Conversion: Multi-Agent Systems coordinate: one agent verifies identity (KYC), another scans for spending anomalies, and a third calculates risk. Decisions happen in milliseconds.
- Benefits & Savings:
- Prevented Losses: The US Treasury recovered $4 Billion in 2024 by switching to ML-driven agentic processes.
- Operational Speed: Loan “Time-to-Decision” drops from days to minutes.
- Live Example: Mastercard/Visa use agents to analyze thousands of data points per transaction to stop fraud before the “swipe” is even completed.
4. Software Engineering (DevOps)
The Use Case: Automated bug fixing and system “self-healing.”
- Current Issues (Without Agents): When a server crashes, on-call engineers are woken up at 3 AM to manually read logs and restart services. CI/CD pipelines break frequently due to minor UI changes.
- After Agent Conversion: Self-healing Agents monitor logs, identify the root cause (e.g., a memory leak), write a temporary patch, and deploy it—notifying the team after the fix is live.
- Benefits & Savings:
- $150k+ Savings: Eliminates the need for a dedicated “Level 1” night-shift support team.
- 95% Maintenance Reduction: Agents “self-heal” test scripts when the UI changes, preventing pipeline stalls.
- Live Example: testRigor uses agents to allow non-technical managers to create tests in plain English that automatically adapt to code changes.
Summary Table: The Economic Impact
| Domain | Before (Human/Bot) | After (AI Agent) | Estimated Saving/Gain |
| E-Commerce | $5-15 per ticket | < $0.50 per ticket | ~80% Cost Reduction |
| Healthcare | 2 hrs paperwork/day | < 15 mins/day | 20% More Patient Capacity |
| Finance | 3-Day Loan Approval | 5-Minute Approval | $4B+ Fraud Prevention |
| Software | Manual Bug Fixing | Autonomous Self-Healing | $120k+ per Engineer |




























































.jpg)